In one of my previous post, I discussed how to use GitHub Actions for automating DBT model build process and hosting DBT documentations on GitHub Pages.
In this post, I will take a closer look into how to use GitHub Actions for CI/CD with Google Cloud Platform, including deploying to Google Cloud Functions, Google Cloud Run, and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
The workflow will look something like below:
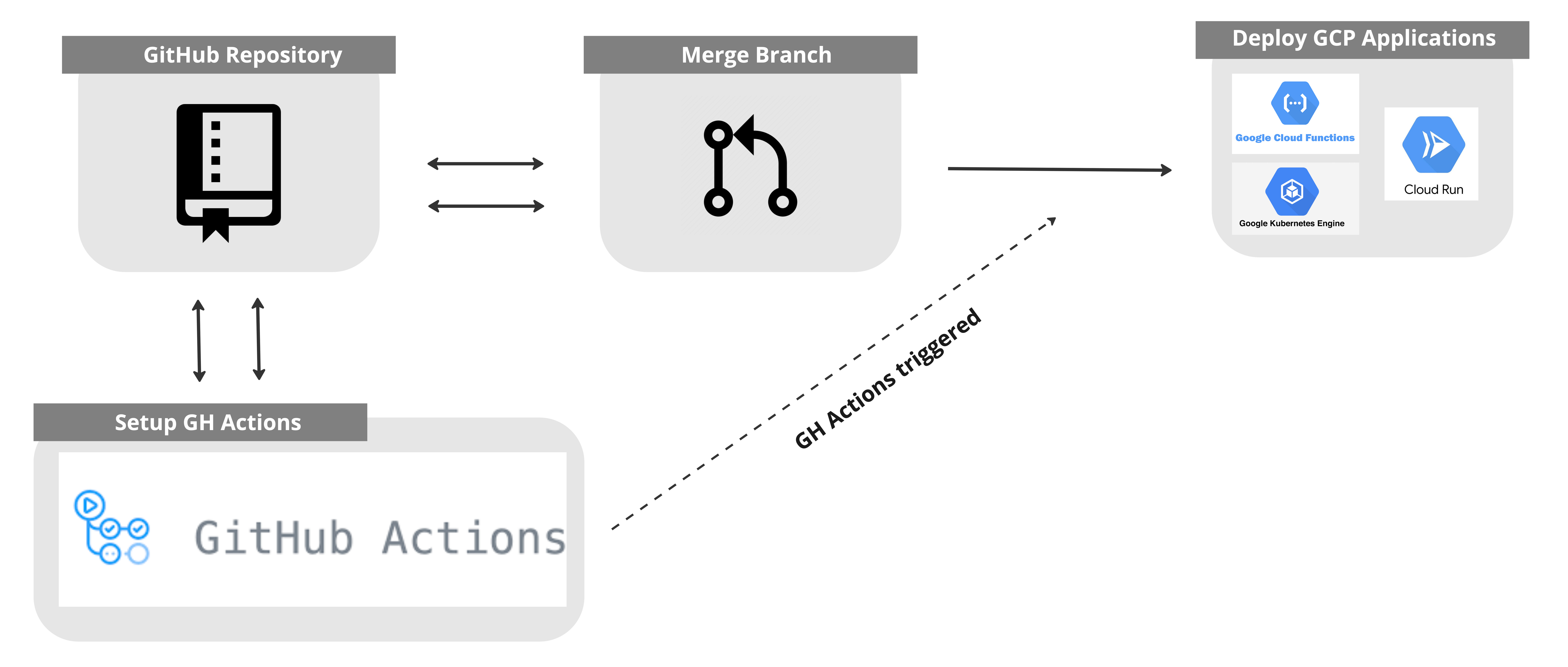
Deploying to Google Cloud Functions
Google Cloud Functions is a serverless execution environment for building and connecting. It is a pay-as-you-go service that automatically scales to zero.
Prerequisites
1 - Set up a new serivce account on GCP for github actions, which will be replaced svc@gcp-prj-123.iam.gserviceaccount.com on the yml file.
2 - Set up Workload Identity Federation on GCP, for more information, please refer to this link.
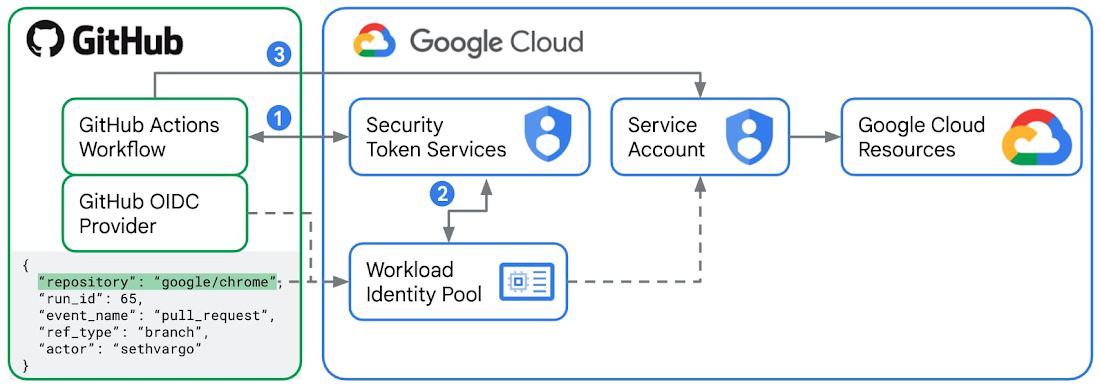
3 - Add sufficient permissions to the service account, e.g. Cloud Functions Developer role.
Setup GitHub Actions
First of all, under the file .gitignore, we should add a line gha-creds-*.json to prevent any creds that generated via the actions process to be pushed to the code.
At the root of your repository, create a .github/workflows folder and create a new yml file, e.g. deploy-cloud-functions.yml.
After adding the following code to the yml file, whenever a pull request is merged to the main branch, the workflow will be triggered.
name: Deploy Cloud Functions
on:
pull_request:
types: [closed]
branches:
- main
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: self-hosted
permissions:
contents: 'read'
id-token: 'write'
deployments: 'write'
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Authenticate to Google Cloud
uses: google-github-actions/auth@v2
with:
token_format: 'access_token'
workload_identity_provider: 'projects/${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}/locations/global/workloadIdentityPools/pool/providers/github-provider'
service_account: 'svc@${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT }}.iam.gserviceaccount.com'
create_credentials_file: true
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v1
with:
version: '>= 493.0.0'
- name: Use gcloud CLI
run: gcloud info
- name: Deploy to gen2 cloud function
run: |
gcloud functions deploy <cloud-function-name> \
--gen2 \
--region=us-central1 \
--runtime=python312 \
--entry-point=<function-in-main-file> \
--trigger-http \
--service-account=svc@${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT }}.iam.gserviceaccount.com
- name: Test cloud function
run: |
gcloud functions call <cloud-function-name> \
--data '{"message": "Hello World"}'
Deploying to Google Cloud Run
Setup GitHub Actions
At the root of your repository, create a .github/workflows folder and create a new yml file, e.g. deploy-cloud-run.yml.
After adding the following code to the yml file, whenever a pull request is merged to the main branch, the workflow will be triggered.
name: Deploy to Cloud Run
on:
pull_request:
types: [closed]
branches:
- main
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: self-hosted
permissions:
contents: 'read'
id-token: 'write'
deployments: 'write'
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Authenticate to Google Cloud
uses: google-github-actions/auth@v2
with:
token_format: 'access_token'
workload_identity_provider: 'projects/${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}/locations/global/workloadIdentityPools/pool/providers/github-provider'
service_account: 'svc@${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT }}.iam.gserviceaccount.com'
create_credentials_file: true
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v1
with:
version: '>= 493.0.0'
- name: Use gcloud CLI
run: gcloud info
- name: Configure Docker
run: gcloud auth configure-docker us-central1-docker.pkg.dev --quiet
- name: Install Skaffold
run: |
curl -Lo skaffold https://storage.googleapis.com/skaffold/releases/latest/skaffold-linux-amd64
sudo install skaffold /usr/local/bin/
- name: Deploy to Cloud Run with Skaffold
env:
SKAFFOLD_DEFAULT_REPO: us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}/my-app
run: |
skaffold run -p production -v info --tag=$GITHUB_SHA
Deploying to Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Setup GitHub Actions
In this exmaple, we are assuming that we have a GKE cluster named autopilot-cluster-1 in the us-central1 zone.
At the root of your repository, create a .github/workflows folder and create a new yml file, e.g. deploy-gke.yml.
After adding the following code to the yml file, whenever a pull request is merged to the main branch, the workflow will be triggered.
name: Deploy to GKE
on:
pull_request:
types: [closed]
branches:
- main
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: self-hosted
permissions:
contents: 'read'
id-token: 'write'
deployments: 'write'
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Authenticate to Google Cloud
uses: google-github-actions/auth@v2
with:
token_format: 'access_token'
workload_identity_provider: 'projects/${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}/locations/global/workloadIdentityPools/pool/providers/github-provider'
service_account: 'svc@${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT }}.iam.gserviceaccount.com'
create_credentials_file: true
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v1
with:
version: '>= 493.0.0'
- name: Use gcloud CLI
run: gcloud info
- name: Install gke gloud plugin
run: |
gcloud components install gke-gcloud-auth-plugin
gke-gcloud-auth-plugin --version
- name: Configure GKE context
run: |
gcloud container clusters get-credentials autopilot-cluster-1 --zone us-central1 --project ${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
- name: Configure Docker
run: gcloud auth configure-docker us-central1-docker.pkg.dev --quiet
- name: Install Skaffold
run: |
curl -Lo skaffold https://storage.googleapis.com/skaffold/releases/latest/skaffold-linux-amd64
sudo install skaffold /usr/local/bin/
- name: Deploy to GKE with Skaffold
env:
SKAFFOLD_DEFAULT_REPO: us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}/my-app
run: |
skaffold run -p production -v info --tag=$GITHUB_SHA
Optionals
Optionally, as a last step, you can add a notification step to notify the team on Webex or any other communication platform of your choice when the deployment fails.
- name: Notify Webex on Deployment Failure
if: ${{ failure() }}
run: |
curl --request POST \
--url 'https://webexapis.com/v1/messages' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer ${{ secrets.WEBEX_BOT_TOKEN }}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data "{
\"roomId\": \"${{ secrets.WEBEX_NOTI_ROOM_ID }}\",
\"markdown\": "Deployment to GKE failed. Please check the GitHub Actions logs for more details."
}"
Sometimes, you may found that trying to do everything in pure bash script/ bash syntax is not the best way to go. In that case, you can use a combination of bash script and Python script to achieve the same goal.
Using sending a webex notification as an example, you can create a Python script notify_webex.py and add the following code to the yml file.
def post_to_webex(markdown_message: str):
"""
Post markdown message to Webex room.
"""
webex_bot_token = os.environ.get("WEBEX_BOT_TOKEN")
webex_room_id = os.environ.get("WEBEX_ROOM_ID")
if not webex_bot_token or not webex_room_id:
logging.error("Webex environment variables are not set")
url = "https://webexapis.com/v1/messages"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {webex_bot_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
}
data = {"roomId": webex_room_id, "markdown": markdown_message}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data)
def main():
# Perform anything is needed
# ...
if failed:
post_to_webex(markdown_message)
else:
logging.info("All processes completed successfully.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- name: Run steps and check for failures
id: run_steps
env:
WEBEX_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.WEBEX_BOT_TOKEN }}
WEBEX_ROOM_ID: ${{ secrets.WEBEX_ROOM_ID }}
run: python py-scripts/notify_webex.py
Which we can see we are passing throught the environment variables to the Python script, and the Python script will use the environment variables to send the notification to the Webex room.
That’s it for now.
Thank you for reading, and have a nice day!



