During some of my previous posts, I talked about setting up different chat bots and integrating LLM with chat bot like Webex and Discord. In this post, I aim to discuss further on how to develop a more interactive chat bot with adaptive cards.
What is Adaptive Card
Adaptive Card is a platform-agnostic schema for card exchange. It is a simple way to create and share card content in a common and consistent way. Adaptive Cards are supported by a wide range of apps and services, including various bot frameworks, Microsoft Teams, and Outlook.
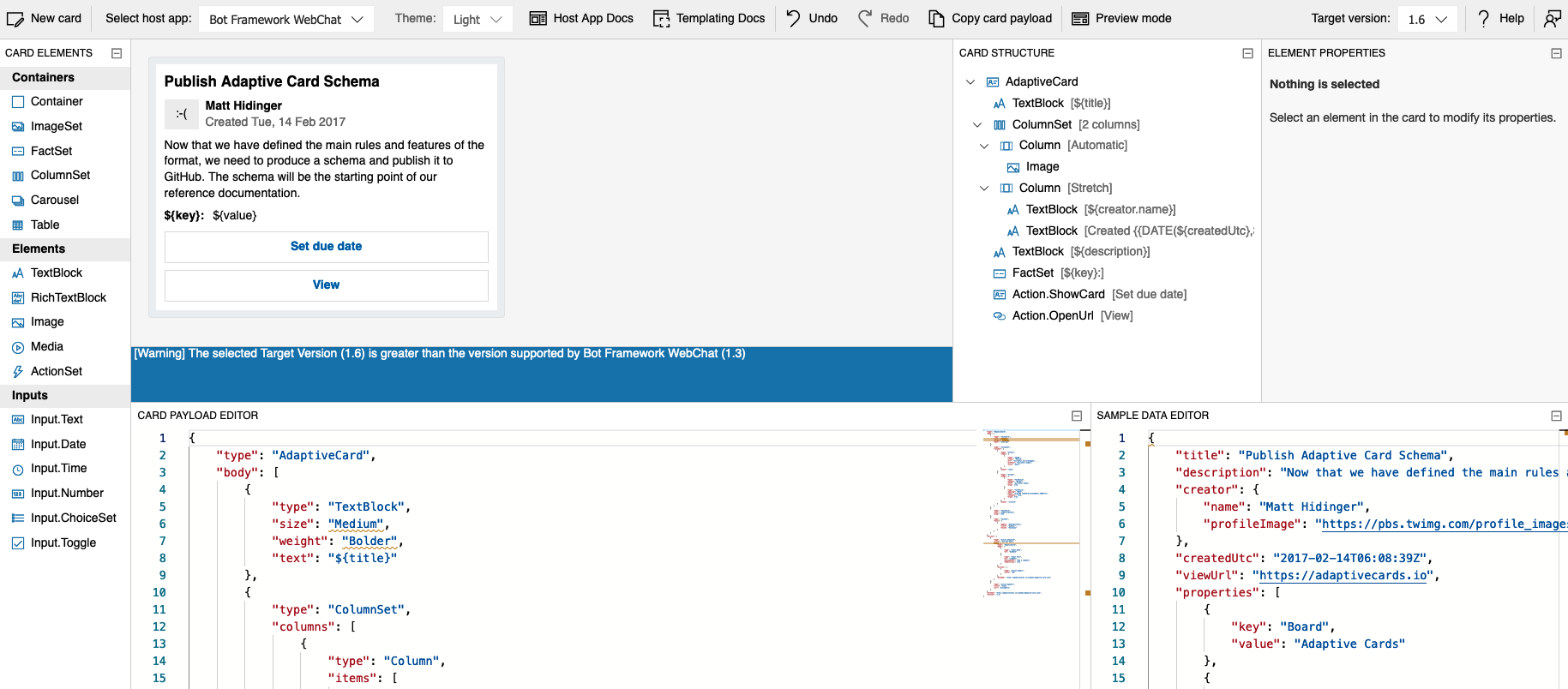
Both Microsoft and Webex provide a web UI to design adaptive cards, either with drag and drop tools or with JSON schema.
Microsoft adaptive cards designer
Webex adaptive card designer
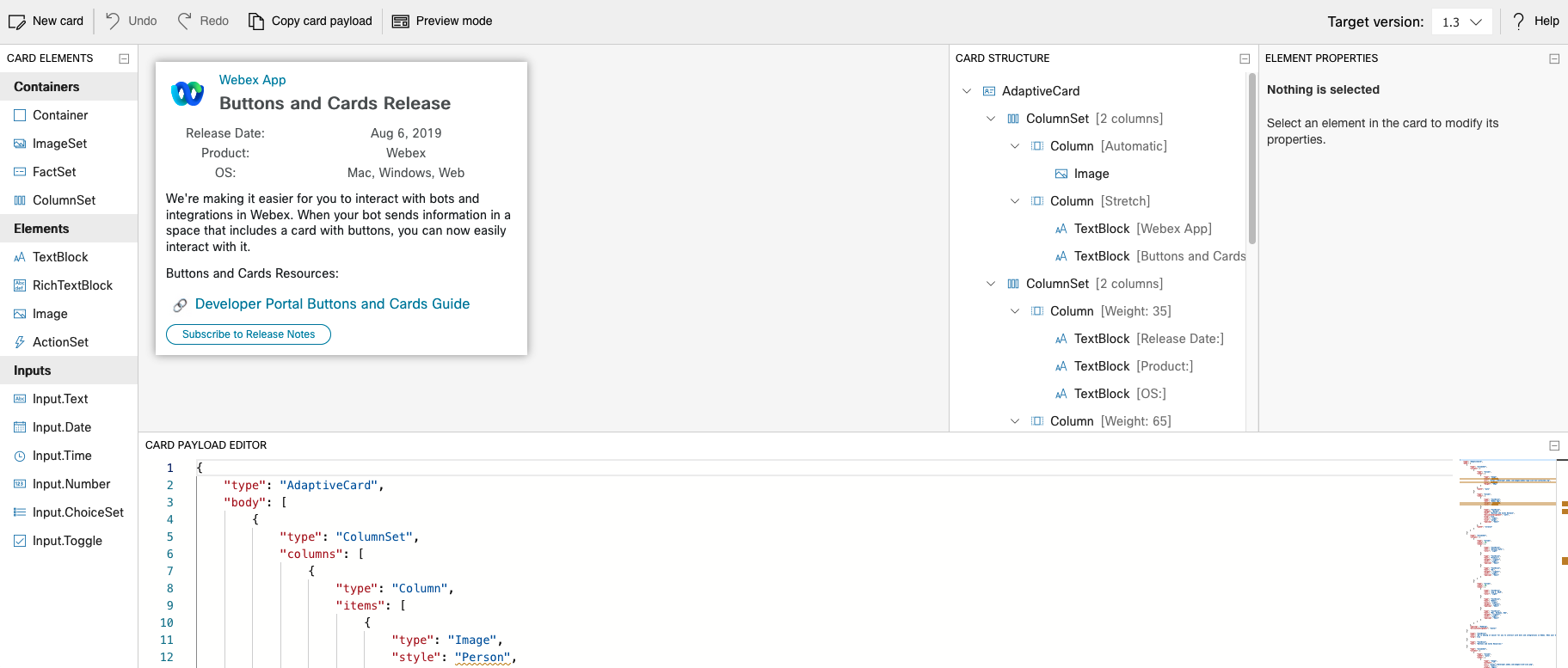
In this article, we will walk through the steps to create an adaptive card, and integrating adaptive card to a webex chat bot.
Example Use Case
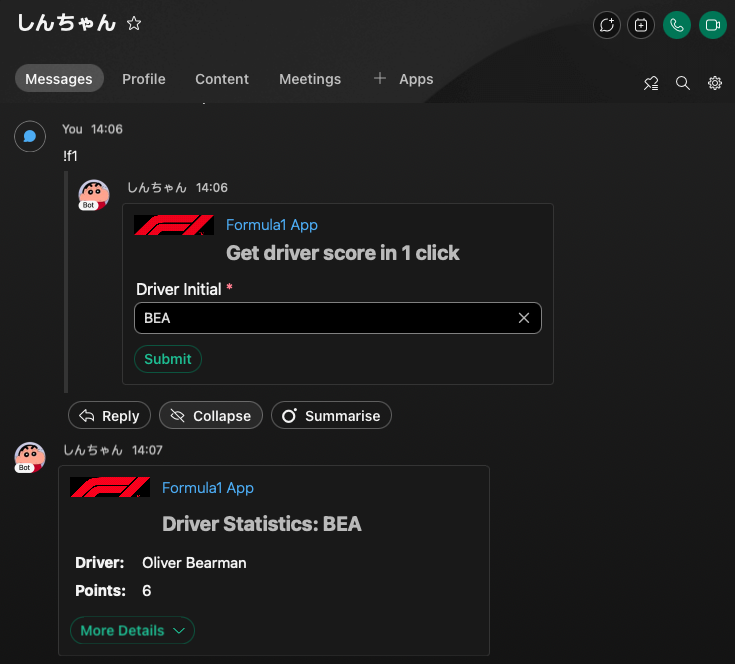
Our example use case is to build a chat bot that can provide the driver’s score in Formula 1. The bot will reply with an adaptive card when a user inputs a command. The card will have an input field for the user to input the driver’s initial, and a button to submit the input.
After the user submits the input, the bot will extract the data to get the driver’s score and reply with the score with an adaptive card.
To follow along, the code is available here
Design an Adaptive Card
We will use the Webex Card Designer to design an adaptive card. The card will have a title, a description, an image, and a button. The button will be used to trigger an action when clicked.
Which the JSON schema of the card is as follows:
{
"type": "AdaptiveCard",
"body": [
{
"type": "ColumnSet",
"columns": [
{
"type": "Column",
"items": [
{
"type": "Image",
"url": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/33/F1.svg/1200px-F1.svg.png",
"size": "Medium",
"height": "20px"
}
],
"width": "auto"
},
{
"type": "Column",
"items": [
{
"type": "TextBlock",
"text": "Formula1 App",
"weight": "Lighter",
"color": "Accent"
},
{
"type": "TextBlock",
"weight": "Bolder",
"text": "Get driver score in 1 click",
"horizontalAlignment": "Left",
"wrap": true,
"color": "Light",
"size": "Large",
"spacing": "Small"
}
],
"width": "stretch"
}
]
},
{
"type": "Input.Text",
"placeholder": "VER",
"isRequired": true,
"errorMessage": "You must reply a valid user inital",
"maxLength": 3,
"id": "driver",
"label": "Driver Initial",
"regex": "[A-Z]"
},
{
"type": "ActionSet",
"actions": [
{
"type": "Action.Submit",
"title": "Submit",
"data": {
"callback_keyword": "!f1"
},
"style": "positive"
}
],
"horizontalAlignment": "Left",
"spacing": "None"
}
],
"$schema": "http://adaptivecards.io/schemas/adaptive-card.json",
"version": "1.3"
}
Code Implementation
To extract driver data from the web, we will use the requests and lxml libraries. The F1Scraper class will scrape the data from the F1 website and store the data in a dictionary. The get_driver_points method will return the driver’s score when given the driver’s initials.
from lxml import html
import requests
class F1Scraper:
def __init__(self):
self.driver_stat_url = (
"https://www.formula1.com/en/results.html/2024/drivers.html"
)
self.all_driver_data, self.driver_initials_to_full_name = (
self.get_all_driver_pts()
)
@staticmethod
def scrape_f1(web_url: str) -> list:
page = requests.get(web_url)
tree = html.fromstring(page.content)
table_rows = tree.cssselect("table.resultsarchive-table tr")
column_headers = [column.text_content().strip() for column in table_rows[0]]
data_rows = []
for row in table_rows[1:]:
data = [column.text_content().strip() for column in row.iterchildren()]
data_rows.append(dict(zip(column_headers, data)))
return data_rows
def get_all_driver_pts(self) -> (dict, dict):
data_rows = self.scrape_f1(self.driver_stat_url)
dr_pts = {}
driver_full_names = {}
for row in data_rows:
dr_name_parts = row["Driver"].replace("\n", "").split()
initials = (
dr_name_parts[-1]
if len(dr_name_parts) == 3
else "".join([name[0] for name in dr_name_parts])
)
full_name = (
" ".join(dr_name_parts[:-1])
if len(dr_name_parts) == 3
else " ".join(dr_name_parts)
)
pts = row["PTS"]
dr_pts[initials] = pts
driver_full_names[initials] = full_name
print("Driver scores retrieved")
return dr_pts, driver_full_names
def get_driver_points(self, initials: str) -> str:
full_name = self.driver_initials_to_full_name.get(initials)
pts = self.all_driver_data.get(initials)
if full_name and pts:
re = f"{full_name} has {pts} points"
else:
re = "Invalid driver initials. Please check the driver initials and try again."
return re
Now we have the adaptive card and the data extraction method ready, the next step is to build the webex bot so that when a user input the command !f1, the bot will reply with the adaptive card that we created above.
When the user submits the driver’s initials, the bot will extract the data and reply with the driver’s score.
from webex_bot.models.command import Command
f1api = F1Scraper()
class Driver(Command):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
command_keyword="!f1",
help_message="!f1 - get f1 driver points",
card=adaptive_cards.DRIVER_CARD,
)
def execute(self, message, attachment_actions, activity):
driver = attachment_actions.inputs["driver"]
details = f1api.get_driver_points(driver)
return details
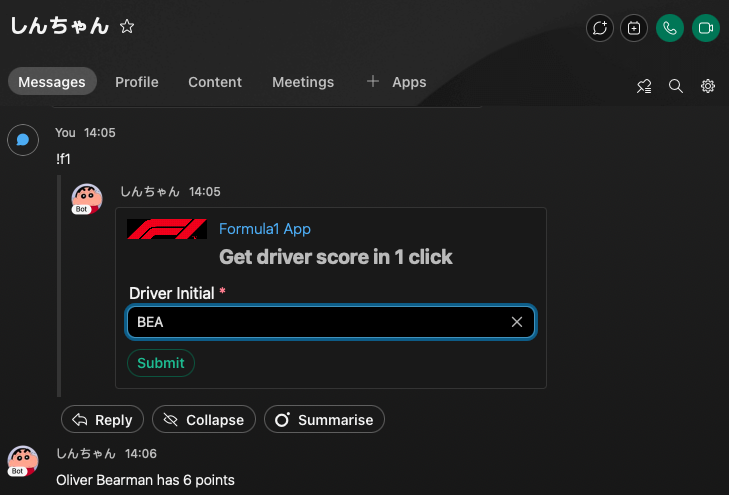
We can also have the bot to reply with an adaptive card instead of a text message. There are various adaptive card libraries available. In this case, we will use the adaptivecardbuilder library to create the adaptive card.
The card will have the driver’s name and points and a button to expand the card for more details.
The code implementation example could look something like this
from webex_bot.models.response import Response
import adaptivecardbuilder as adcb
card = adcb.AdaptiveCard()
card.add(adcb.TextBlock(text="Driver Score", size="Large", weight="Bolder"))
# ... Rest of the logic
card_data = adcb.json.loads(adcb.asyncio.run(card.to_json()))
card_payload = {
"contentType": "application/vnd.microsoft.card.adaptive",
"content": card_data,
}
response = Response()
response.text = "F1 Card"
response.attachments = card_payload
To put everything together, in the commands.py file we can have the following.
class Driver(Command):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
command_keyword="!f1",
help_message="!f1 - get f1 driver points",
card=adaptive_cards.DRIVER_CARD,
)
def execute(self, message, attachment_actions, activity):
driver = attachment_actions.inputs["driver"]
logger.info(f"{activity['actor']['emailAddress']} enquiring driver: {driver}")
details = f1api.get_driver_points(driver)
logger.info(f"Resposne: {details}")
match = re.compile(r"(.*) has (\d+) points").search(details)
card = adcb.AdaptiveCard()
card.add(
[
adcb.ColumnSet(),
adcb.Column(width="auto"),
adcb.Image(
url="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/33/F1.svg/1200px-F1.svg.png",
size="Medium",
height="20px",
),
"<",
adcb.Column(width="stretch"),
adcb.TextBlock(text="Formula1 App", color="Accent", weight="Lighter"),
adcb.TextBlock(
text=f"Driver Statistics: {driver}",
size="Large",
weight="Bolder",
color="Light",
),
"<",
"<",
adcb.ColumnSet(),
adcb.Column(width="stretch"),
adcb.FactSet(),
adcb.Fact(title="Driver:", value=f"{match.group(1)}"),
adcb.Fact(title="Points: ", value=f"{match.group(2)}"),
"^",
adcb.ActionSet(),
adcb.ActionShowCard(title="More Details", style="positive"),
adcb.ColumnSet(),
adcb.Column(width="stretch"),
adcb.FactSet(),
adcb.Fact(
title="Visit official website",
value="[Click here](https://www.formula1.com/)",
),
]
)
card_data = adcb.json.loads(adcb.asyncio.run(card.to_json()))
card_payload = {
"contentType": "application/vnd.microsoft.card.adaptive",
"content": card_data,
}
response = Response()
response.text = "Test Card"
response.attachments = card_payload
return response
And to run the bot, we can have the following in the main.py file.
from webex_bot.webex_bot import WebexBot
from commands import *
from settings import app_config
bot = WebexBot(app_config.WEBEX_TOKEN)
bot.add_command(Driver())
if __name__ == "__main__":
bot.run()
And that’s it! We have successfully built a chat bot that can provide the driver’s score in Formula 1. The bot will reply with an adaptive card when a user inputs a command. The card will have an input field for the user to input the driver’s initial, and a button to submit the input. After the user submits the input, the bot will extract the data to get the driver’s score and reply with the score with an adaptive card.

Thank you for reading and have a nice day!