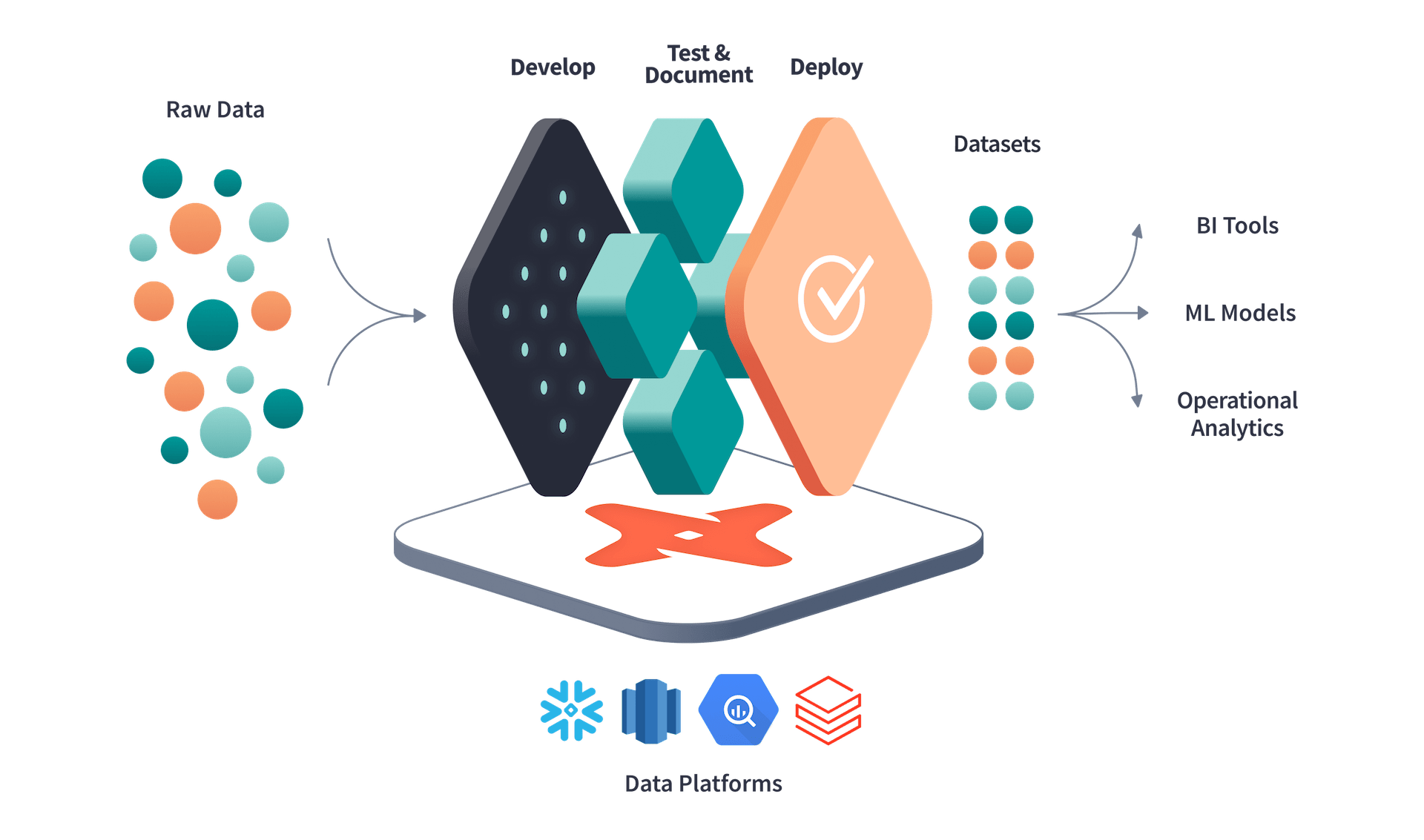
Last time we talk about some of the basic dbt functionalities, in this blog post, I want to talk about how we can use github workflows to automate dbt.
For a lot of dbt-core users who are not using the dbt cloud version, integrating dbt with github workflows is an alternative to automate dbt models & tests run, also for hosting the documentation page.
In this post, we will look at automating the models build and testing process by GitHub Actions, also using the github pages action to host the dbt documentation page on github.
What is github workflow?
According to the official github website, GitHub Actions is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform that allows you to automate your build, test, and deployment pipeline. You can create workflows that build and test every pull request to your repository, or deploy merged pull requests to production.
Set up dbt with github workflow
Assuming our repo looks something like this, a snowflake dev warehouse with bronze, silver and gold schema.
├── README.md
├── bronze_schema
│ ├── analyses
│ ├── dbt_packages
│ ├── dbt_project.yml
│ ├── logs
│ ├── macros
│ ├── models
│ ├── packages.yml
│ ├── seeds
│ ├── snapshots
│ ├── target
│ └── tests
├── silver_schema
│ ├── analyses
│ ├── dbt_packages
│ ├── dbt_project.yml
│ ├── logs
│ ├── macros
│ ├── models
│ ├── packages.yml
│ ├── seeds
│ ├── snapshots
│ ├── target
│ └── tests
└── gold_schema
├── analyses
├── dbt_packages
├── dbt_project.yml
├── logs
├── macros
├── models
├── packages.yml
├── seeds
├── snapshots
├── target
└── tests
Job Automation
1 - Set up workflow yml file
On you github dbt project repo, create a new folder .github/workflows/job-automation.yml.
Alternatively, you can also directly click on Actions > New actions, to import the workflow yml.
Under job-automation.yml, we will have to add below, the workflow is now set to run either on-demand manual trigger or daily at 7 am.
name: job-automation
on:
workflow_dispatch:
schedule:
- cron: 0 7 * * *
env:
DBT_PROFILES_DIR: ./
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_PW: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_PW }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ROLE: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ROLE }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_DATABASE: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_DATABASE }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_BRONZE_SCHEMA: bronze_schema
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_SILVER_SCHEMA: silver_schema
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_GOLD_SCHEMA: gold_schema
jobs:
job-automation:
runs-on: self-hosted
steps:
- name: Check out
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: "3.9.6"
# pip install dbt
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
pip install dbt-core==1.3.1
pip install dbt-snowflake==1.3.0
dbt deps --project-dir bronze_schema
dbt deps --project-dir silver_schema
dbt deps --project-dir gold_schema
# dbt related commands -
- name: Run dbt models
run: dbt run --project-dir bronze_schema --models folder.subfolder.model_name
- name: Test dbt models
run: dbt test --project-dir gold_schema --select folder.subfolder.model_name
2 - Set up secrets/ env var for job
Navigate to Settings > Security > Actions, add all your secrets and/ or env variables for the job. In our case this time, we will be setting the repository’s secret.
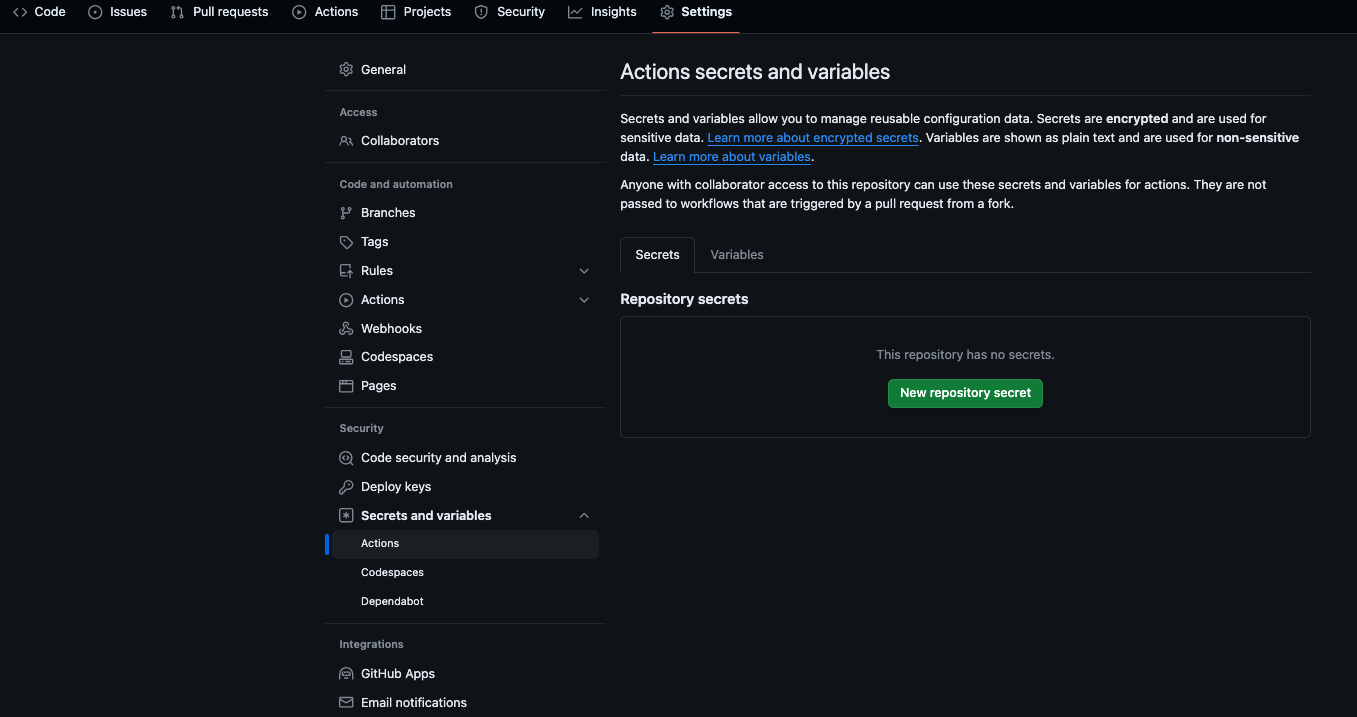
3 - Set up profiles.yml
On the root of the dbt github repo, create a profiles.yml
It will look somthing like this
bronze_schema:
outputs:
dev:
account: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT') }}"
database: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_DATABASE') }}"
password: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_PW') }}"
role: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ROLE') }}"
schema: BRONZE_SCHEMA
threads: 1
type: snowflake
user: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME') }}"
warehouse: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE') }}"
target: dev
silver_schema:
outputs:
dev:
account: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT') }}"
database: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_DATABASE') }}"
password: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_PW') }}"
role: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ROLE') }}"
schema: SILVER_SCHEMA
threads: 1
type: snowflake
user: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME') }}"
warehouse: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE') }}"
target: dev
gold_schema:
outputs:
dev:
account: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT') }}"
database: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_DATABASE') }}"
password: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_PW') }}"
role: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ROLE') }}"
schema: GOLD_SCHEMA
threads: 1
type: snowflake
user: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME') }}"
warehouse: "{{ env_var('DBT_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE') }}"
target: dev
And with the above set up, we now are able to automate our dbt models.
As an extra, we can also configure the workflow so that if there are any models failed, the workflow also send a notification message to a channel like emails, slack, telegram, webex etc.
The example below shows a task that send a notification message to a webex space when there are failed dbt model during the build process.
name: job-automation
on:
workflow_dispatch:
schedule:
- cron: 0 7 * * *
env:
DBT_PROFILES_DIR: ./
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_PW: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_PW }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ROLE: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ROLE }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_DATABASE: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_DATABASE }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_BRONZE_SCHEMA: bronze_schema
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_SILVER_SCHEMA: silver_schema
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_GOLD_SCHEMA: gold_schema
jobs:
job-automation:
runs-on: self-hosted
steps:
- name: Check out
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: "3.10"
# pip install dbt
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
pip install dbt-core==1.3.1
pip install dbt-snowflake==1.3.0
dbt deps --project-dir bronze_schema
dbt deps --project-dir silver_schema
dbt deps --project-dir gold_schema
- name: Build dbt models and check for failures
id: dbt_run
run: |
declare -A SCHEMA_MODELS
SCHEMA_MODELS[bronze_schema]="project.model project.model2 project.model3"
SCHEMA_MODELS[silver_schema]="project.model project.model2"
SCHEMA_MODELS[gold_schema]="project.model"
FAILED_MODELS=""
for PROJECT_DIR in "${!SCHEMA_MODELS[@]}"; do
MODELS=(${SCHEMA_MODELS[$PROJECT_DIR]})
for MODEL in "${MODELS[@]}"; do
if ! dbt run --project-dir $PROJECT_DIR --models $MODEL; then
FAILED_MODELS+="${PROJECT_DIR^^}.${MODEL^^} \\n"
fi
done
done
if [ -n "$FAILED_MODELS" ]; then
echo "FAILED_MODELS=$FAILED_MODELS" >> $GITHUB_ENV
fi
continue-on-error: true
- name: Notify Webex with dbt build result
if: env.FAILED_MODELS != ''
run: |
curl --request POST \
--url 'https://webexapis.com/v1/messages' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer ${{ secrets.WEBEX_BOT_TOKEN }}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data "{
\"roomId\": \"${{ secrets.WEBEX_NOTI_ROOM_ID }}\",
\"markdown\": \"The GitHub Actions DBT build workflow failed with the following DBT model(s):\\n\\n$FAILED_MODELS\"
}"
- name: Run dbt tests and check for failures
id: dbt_test
run: |
declare -A SCHEMA_TESTS
SCHEMA_MODELS[bronze_schema]="project.model project.model2 project.model3"
SCHEMA_MODELS[silver_schema]="project.model project.model2"
SCHEMA_MODELS[gold_schema]="project.model"
FAILED_TESTS=""
for PROJECT_DIR in "${!SCHEMA_TESTS[@]}"; do
TESTS=(${SCHEMA_TESTS[$PROJECT_DIR]})
for TEST in "${TESTS[@]}"; do
if ! dbt test --project-dir $PROJECT_DIR --select $TEST; then
FAILED_TESTS+="${PROJECT_DIR^^}.${TEST^^} \\n"
fi
done
done
if [ -n "$FAILED_TESTS" ]; then
echo "FAILED_TESTS=$FAILED_TESTS" >> $GITHUB_ENV
fi
continue-on-error: true
- name: Notify Webex with dbt test result
if: env.FAILED_TESTS != ''
run: |
curl --request POST \
--url 'https://webexapis.com/v1/messages' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer ${{ secrets.WEBEX_BOT_TOKEN }}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data "{
\"roomId\": \"${{ secrets.WEBEX_NOTI_ROOM_ID }}\",
\"markdown\": \"The dbt test step has failed in the GitHub Actions workflow with the following DBT test(s):\\n\\n$FAILED_TESTS\"
}"
Hosting Documentaion Page on GitHub
Next, let’s work on building a workflow that build a gituhb page to host the dbt documentation for all bronze, silver and gold schemas.
Firstly, we will have to set the pages setting of the repo under settings > pages
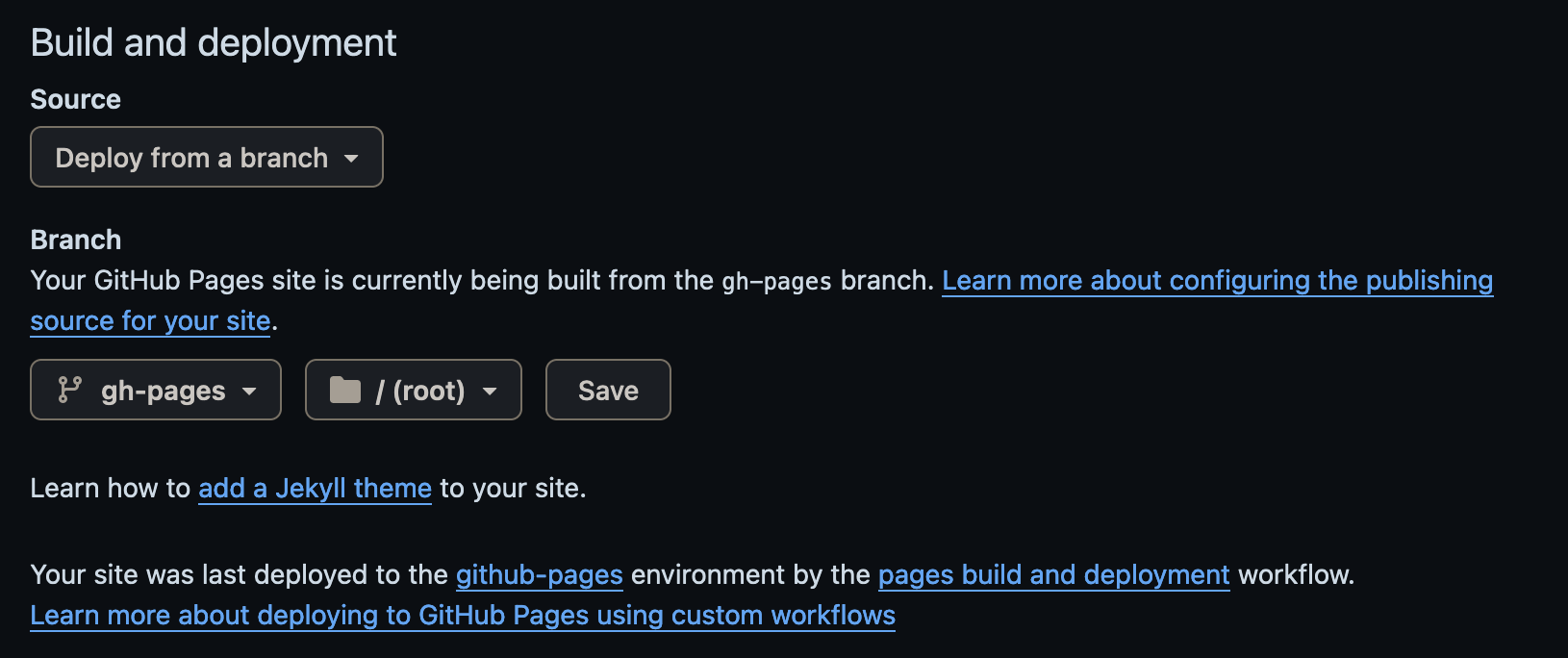
After that, under the folder .github/workflows dir, we can open a new yml workflow file looks like below:
name: docs
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
env:
DBT_PROFILES_DIR: ./
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_PW: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_PW }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ROLE: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_ROLE }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_DATABASE: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_DATABASE }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE: ${{ secrets.DBT_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE }}
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_BRONZE_SCHEMA: bronze_schema
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_SILVER_SCHEMA: silver_schema
DBT_SNOWFLAKE_GOLD_SCHEMA: gold_schema
jobs:
docs:
name: docs
runs-on: self-hosted
steps:
- name: Check out
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: "3.10"
# pip install dbt
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
pip install dbt-core==1.3.1
pip install dbt-snowflake==1.3.0
dbt deps --project-dir bronze_schema
dbt deps --project-dir silver_schema
dbt deps --project-dir gold_schema
- name: build single html
run: |
dbt docs generate --project-dir bronze_schema
dbt docs generate --project-dir silver_schema
dbt docs generate --project-dir gold_schema
python dbt-docs.py
- name: Deploy to GitHub Pages
if: success()
uses: crazy-max/ghaction-github-pages@v3
with:
target_branch: gh-pages
build_dir: target
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GH_TOKEN }}
Then under the root dir ./ we need to have a python file called dbt-docs.py
What this scirpt essentially doing is to merge the front end manifests of each schema to a consolidated file so that the page can be rendered properly.
import json
import os
import shutil
from pathlib import Path
from functools import reduce
class SchemaMerger:
def __init__(self, schemas):
self.schemas = schemas
self.base_dir = Path(os.getcwd())
self.new_target_dir = self.base_dir / "target"
self.search_str = (
'o=[i("manifest","manifest.json"+t),i("catalog","catalog.json"+t)]'
)
self.combined_manifest = {
"nodes": {},
"sources": {},
"exposures": {},
"metrics": {},
"selectors": {},
"tests": {},
"child_map": {},
"docs": {},
"disabled": {},
}
self.combined_catalog = {
"nodes": {},
"sources": {},
"exposures": {},
"metrics": {},
}
@staticmethod
def merge_dicts(a, b):
for key, value in b.items():
if isinstance(value, dict):
if key in a and isinstance(a[key], dict):
SchemaMerger.merge_dicts(a[key], value)
else:
a[key] = value
else:
a[key] = value
def load_and_merge_json(self, file_path, combined):
with open(file_path, "r") as f:
data = json.load(f)
self.merge_dicts(combined, data)
return combined
@staticmethod
def replace_content_in_file(file_path, search_str, new_str):
with open(file_path, "r") as f:
content = f.read()
new_content = content.replace(search_str, new_str)
with open(file_path, "w") as f:
f.write(new_content)
def run(self):
self.new_target_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
shutil.copy(
self.base_dir / self.schemas[0] / "target" / "index.html",
self.new_target_dir / "index.html",
)
self.combined_manifest = reduce(
lambda combined, schema: self.load_and_merge_json(
self.base_dir / schema / "target" / "manifest.json", combined
),
self.schemas,
self.combined_manifest,
)
self.combined_catalog = reduce(
lambda combined, schema: self.load_and_merge_json(
self.base_dir / schema / "target" / "catalog.json", combined
),
self.schemas,
self.combined_catalog,
)
with open(self.new_target_dir / "manifest.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(self.combined_manifest, f)
with open(self.new_target_dir / "catalog.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(self.combined_catalog, f)
new_str = (
"o=[{label: 'manifest', data: "
+ json.dumps(self.combined_manifest)
+ "},{label: 'catalog', data: "
+ json.dumps(self.combined_catalog)
+ "}]"
)
self.replace_content_in_file(
self.new_target_dir / "index.html", self.search_str, new_str
)
sf_schemas = ["bronze_schema", "silver_schema", "gold_schema"]
merger = SchemaMerger(sf_schemas)
merger.run()
And that’s it, when we now merge code to the main branch, the dbt documetation page will re-build and deploy automatically.
Some final thoughts…
This is just one use case; there’s so much more GitHub Actions can do, such as ensuring code quality and security on branches based on git push, automating deployment on merging branches, etc.
That’s it for now.
Thank you for reading, and have a nice day!